The circular economy is now at the center of global sustainability strategies, especially when it comes to plastic. This material, essential in everyday life but criticized for its environmental impact, can become a precious resource if managed in a virtuous cycle of reuse, recycling and regeneration.
What the circular economy applied to plastic really means, what are the benefits for the environment and for businesses and what challenges remain to be faced?
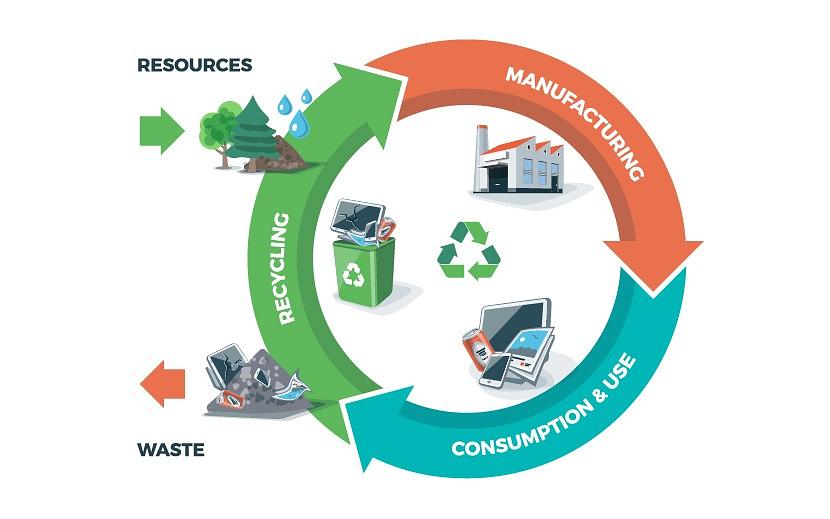
What is circular economy?
The circular economy is a production and consumption model that aims to minimize waste by extending the useful life of materials and products. It is opposed to the traditional linear model based on: Produce – Use – Dispose.
In the circular economy, on the other hand, priority is given to:
- Waste reduction
- Reuse of materials
- Efficient recycling
- Energy recovery (when recycling is not possible)
Circular economy and plastic: why is it crucial?
Plastic is one of the most discussed materials in the environmental context:
-Only about 9% of the plastic produced in the world is recycled.
-The rest ends up in landfills, in incinerators or, worse, in the environment.
The circular economy applied to plastic aims to:
-Prolong the life of plastic through recycling.
-Reduce dependence on virgin raw materials.
-Limit the production of unmanageable waste.
Circular economy strategies in plastics
- Product eco-design
Creation of easy-to-recycle packaging.
Reduction of the amount of plastic used in products.
- Efficient separate waste collection
Capillary and digitalized collection systems to track plastic along the entire supply chain.
- Mechanical and chemical recycling
Mechanical recycling allows plastic to be regenerated for new uses.
Chemical recycling allows highly contaminated or multi-material plastic to be recovered.
- Regeneration and re-marketing
Specialized companies such as Germanplast transform plastic waste into new resources through sorting, shredding and granulation processes.
- Producer responsibility
Extended producer responsibility (EPR) systems to ensure the correct end-of-life of plastic products.
The benefits of circular economy in plastics
- Reduction of pollution: less plastic in landfills, in the oceans and in ecosystems.
- Saving of resources: less oil extraction for the production of virgin plastic.
- Reduction of CO₂ emissions: recycling and regeneration consume less energy than the production of new plastic.
- Economic opportunities: growth of sectors such as recycling, regeneration and eco-design.
- Innovation and competitiveness: companies that adopt circular models are more sustainable and more competitive at European and global level.
The challenges still open
- Poor quality of collected plastic: presence of contaminants and non-recyclable materials.
- Insufficient collection in developing countries.
- Limited demand for recycled plastic compared to virgin plastic.
- Need for innovation in chemical recycling processes.
What is Europe doing for circular plastics?
The European Union has launched the Circular Plastics Alliance, with the aim of:
1.Using at least 10 million tonnes of recycled plastic in new products by 2025.
2.Promoting design for recycling.
3.Developing modern collection and treatment infrastructure.
The EU strategy for plastics also bans some single-use products and aims to incentivize companies that invest in recycling.
Germanplast has been committed for years to transforming plastic waste into new quality raw materials, through:
- New or reconditioned machinery suitable for the customer's project
- Advanced sorting processes
- Collaborations with European and non-European companies for the sustainable management of plastic
Adopting the circular economy is no longer a choice, but a necessity to build a cleaner and more responsible future.
The circular economy applied to plastic represents the key to reducing environmental impact and transforming plastic from waste to resource. Companies that, like Germanplast, invest in innovation and recycling contribute concretely to a more sustainable, competitive and responsible system.